Catalog Archive
Auction 106, Lot 153
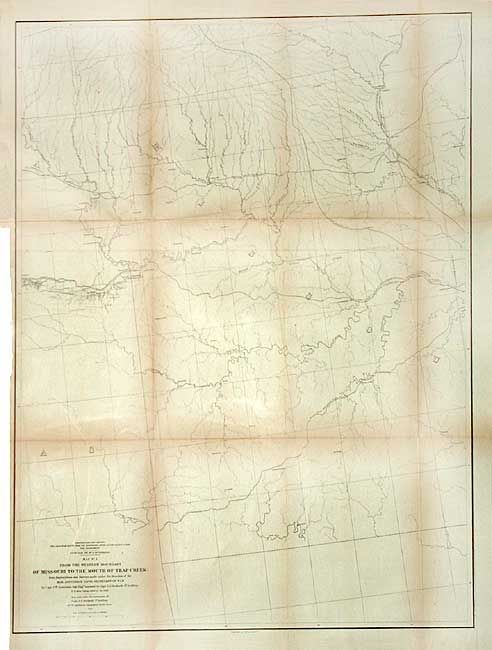
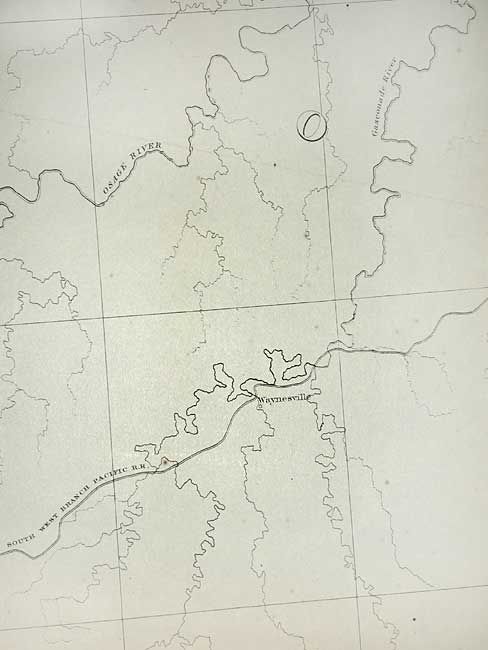
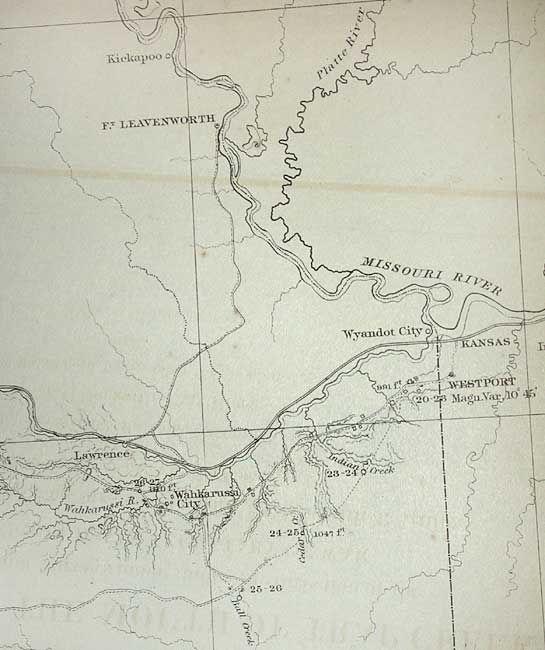
"Map No. 1 From the Western Boundary of Missouri to the Mouth of Trap Creek…", Gunnison, John William [Capt.]
Subject: United States - Western
Period: 1855 (dated)
Publication: U.S. Pacific Railroad Surveys
Color: Black & White
Size:
23.5 x 31 inches
59.7 x 78.7 cm
Download High Resolution Image
(or just click on image to launch the Zoom viewer)
(or just click on image to launch the Zoom viewer)